Author: Ashima Yadav, Dinesh Kumar Vishwakarma
A significant goal of sentiment analysis is to classify and analyze the reviews related to products, hotels, online booking sites, e-commerce sites, social media, etc.
Singla et al. (2017) They have categorized text into positive and negative polarity, and have also include sentiments of anger, anticipation, fear, joy, sadness, disgust, surprise, and trust. The classification is done through SVM resulting in an accuracy of 84.85%. These results are useful for manufacturers as they can work on the feedback to improve the quality of product.
Different from these surveys, this review aims to cover the significant and widespread approaches which are introduced recently in the field of sentiment analysis using deep learning.
This survey provides a comprehensive review of the existing literature on sentiment analysis with deep learning architecture. The significant contribution of this survey can be summarized as:
-
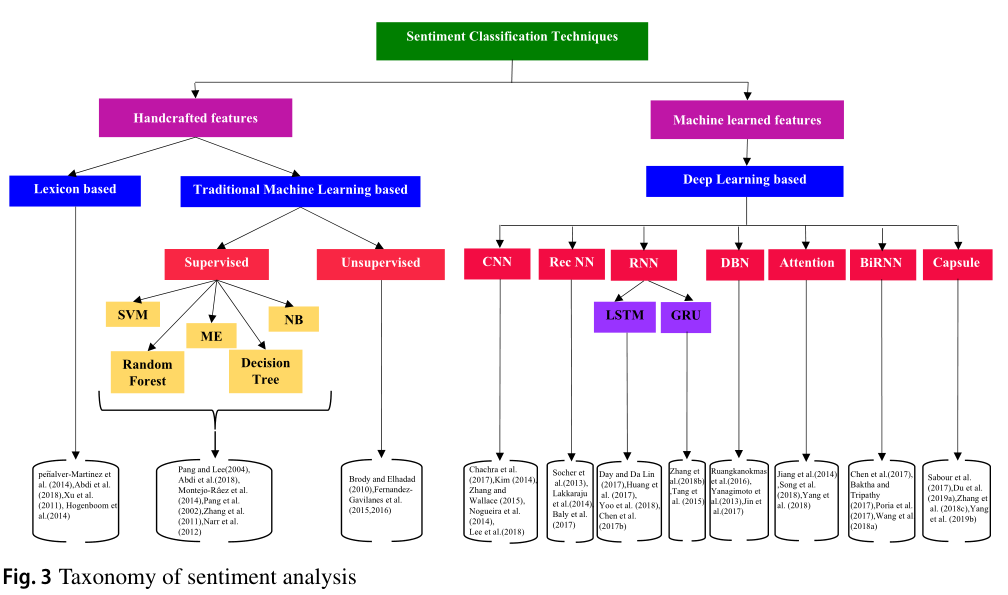
Outlined a taxonomy for sentiment classification (Fig. 3), which includes methods using handcrafted and machine-learned feature-based approaches.
-
Discuss the architecture of various deep learning-based approaches to summarize the notable work and highlight the popular deep learning-based architecture used by various researchers for sentiment analysis.
-
Present the vital sentiment analysis tasks and identify why deep learning models are increasingly applied to them.
-
Identify the popular sentiment analysis datasets, the accuracy obtained on them, and discuss the need for creating own corpus for sentiment analysis.
-
•Outlined a taxonomy for sentiment classification (Fig.3), which includes methods using
-
handcrafted and machine-learned feature-based approaches.
-
•Discuss the architecture of various deep learning-based approaches to summarize the
-
notable work and highlight the popular deep learning-based architecture used by various
-
researchers for sentiment analysis.
-
•Present the vital sentiment analysis tasks and identify why deep learning models are
-
increasingly applied to them.
-
•Identify the popular sentiment analysis datasets, the accuracy obtained on them, and discuss
-
the need for creating own corpus for sentiment analysis.
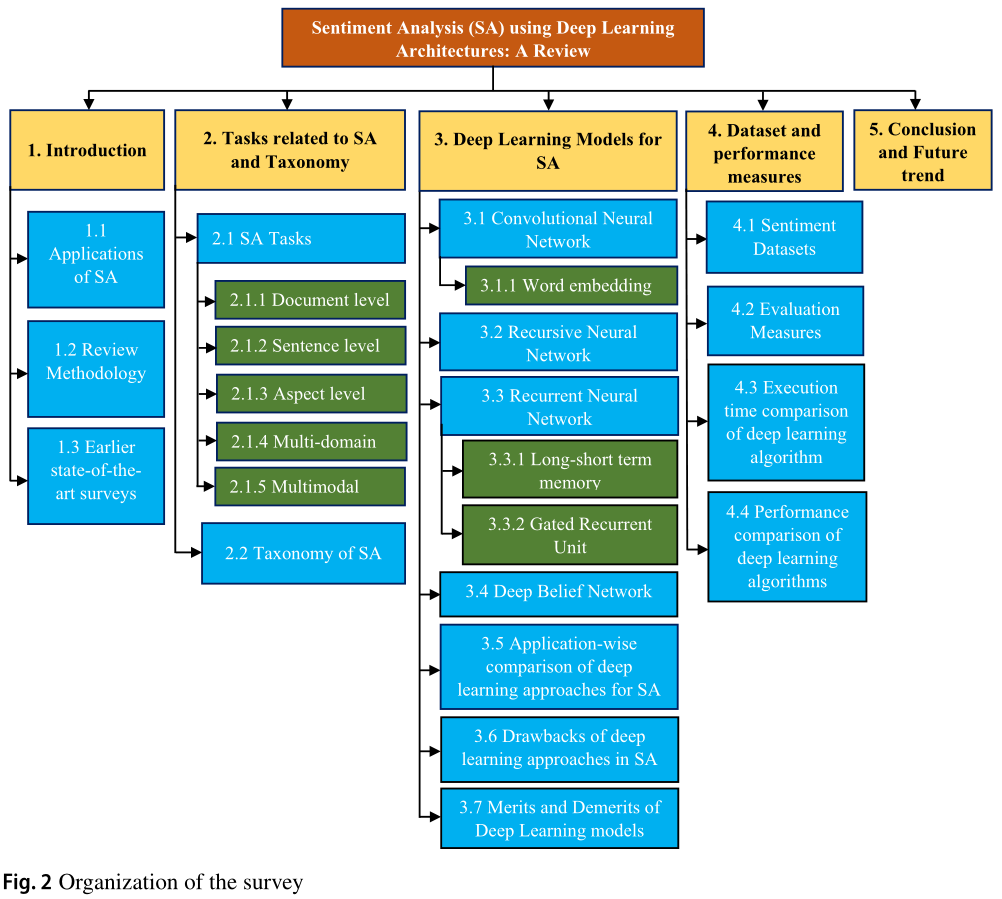
The organization of the survey is shown in Fig. 2.
The sentiment analysis tasks can be categorized into two parts: core(or major) tasks which are referred as the basic sentiment analysis tasks, and second category includes the sub-tasks that are called sub-categories of the major tasks.
Document-level sentiment classification
This level of classification takes the whole document as a primary unit of information focusing on one topic or object. The document is further categorized into positive polarity or negative polarity . Thus, an overall sentiment of text can be generated.
Disadvantage
Disadvantage is difficult to extract the different polarity or sentiment about distinct entities separately .
Sentence-level sentiment classification:
A sentence is classification into subjective type or objective type.
Subjective
Express an opinion towards an entity. Hence, it is considered as a subjective statement that can be further classified into different polarities.
Objective
Factual statement
Aspect-level sentiment classification
(feature-based sentiment analysis, entity-based sentiment analysis) This sentiment analysis task includes the identification of features or aspects in a sentence (which is a user-generated review of an entity) and categorizing the features as positive or negative. The sentiment-target pairs are first identified, then they are classified into different polarities, and finally, sentiment values for every aspect are clubbed.
Multi-domain sentiment classification
The word $ domain $ is referred as a set of documents that are related to a specific topic. Multi-domain sentiment classification focuses on transferring information from one domain to the next domain. The models are first trained in source domain; the knowledge is then transferred and explored in another domain.
Multimodal sentiment classification
Different people express their sentiments or opinions in different ways. Earlier, the text was considered as the primary medium to express an opinion. This is known as a unimodal approach. With the advancement of technology and science, people are now shifting towards visual (videos, images, or clips) and audio (speech) modalities to express their sentiments. Combining or fusing more than one modalities for detecting the opinion is known as multi-modal sentiment analysis. Hence, researchers are now focusing on this direction for improving the sentiment classification process.
Due to the enormous data available on social media in different forms like videos, audios, photos for expressing sentiment on social media platforms, the conventional approach for text-based sentiment analysis was progressed into compound models of multimodal sentiment analysis. Hence, mining the opinions expressed in different modalities became a crucial approach.
The popular models applied to sentiment analysis (SA) tasks can be summarised as:
-
For document-level sentiment classification, CNN followed by LSTM has shown the highest on the various dataset.
-
For sentence-level sentiment classification and aspect-level sentiment classification,researchers have majorly focused on RNN(Particularly LSTM).
-
For multi-domain sentiment classification, LSTM has given good results, and for multi-modal sentiment classification, CNN and RNN are popular deep learning models. Hence, RNN models are the most sought-after and popular choice for sentiment analysis among researchs.
-
Further, we can see that LSTM is popular applied for text-based sentiments, and CNN models have shown good results for image sentiment. For multimodal data, CNN+LSTM followed by fusion becomes the desired approach.
However, the choice of a specific deep learning model may still depend on the various number of factors like the amount of data available, the number of hidden units (nodes) required for the problem, etc.
Future extraction
including handcrafted features and machine-learned features.
Machine-learned features
can be categorized into traditional machine learning-based approaches and deep learning-based approaches.
Machine learning-based methods
include Support Vector Machine (SVM), Naive Bayes (NB), Maximum Entropy (ME), Decision tree learning, and Random Forests. They are further categorized into supervised and unsupervised learning methods.
It becomes evident that the number of established approaches for supervised learning is more as compound to unsupervised learning-based approaches.
Deep learning-based approaches
include Convolution Neural Network, Recursive Neural Network, Recurrent Neural Network (which includes LSTM and GRU), Deep Belief Networks, Attention-based networks, Bi-directional Recurrent Neural Network, and Capsule Network.
Deep Learning reduces the burden of design as when the network learns, it automatically creates the required features for the classification process.
At present, a massive amount of data is being generated. traditional machine learning-based approaches fail to perform. On the contrary, deep learning models outperform the machine learning approaches as they can be trained to learn more features with large datasets. This justifies the fact that deep learning models show improved performance than traditional machine learning models.
Convolutional neural networks(CNNs)
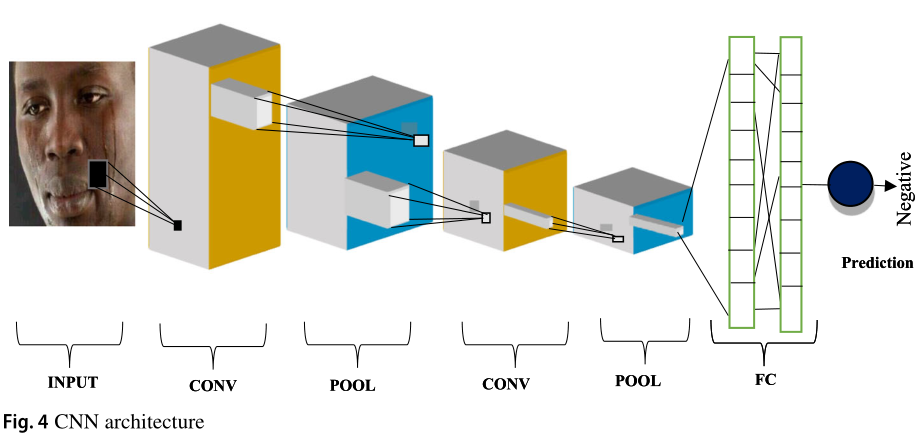
belong to the class of neural networks and have shown significant success and innovation in computer vision and image processing. The fundamental architecture of CNN is displayed in Fig. 4.
Embeddings
It can be obtained using Skip Gram model and Common Bag of words(CBOW).
CBOW
The model predicts the current word from surrounding context words.
Skip Gram
The model predicts the surrounding context words from the current word.
Recursive neural networks (RecNNs)
It belongs to the category of the network, that learns a directed acyclic graph structure (e.g., tree structure ).
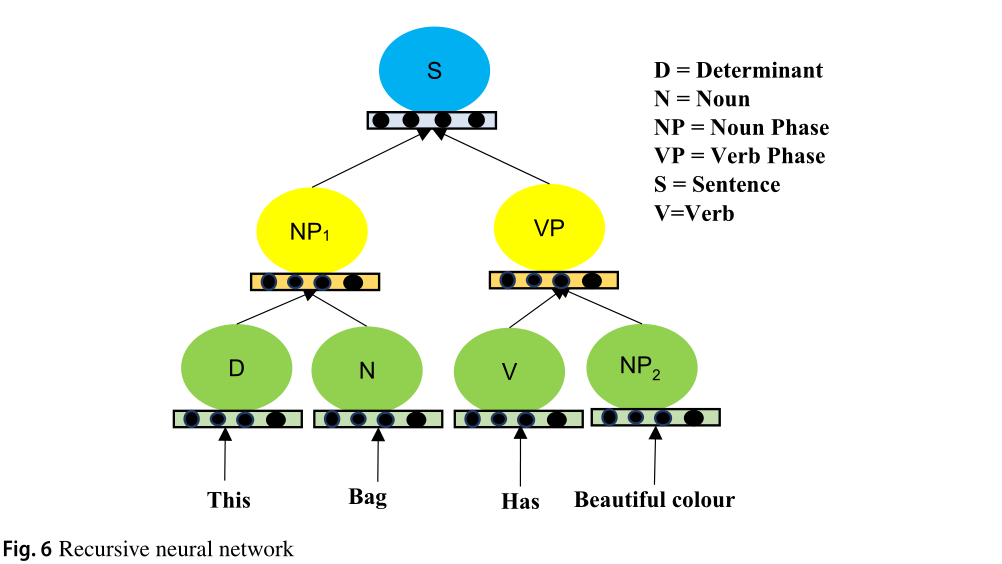
Figure 6 shows a Rec NN in which whenever a sequence of n-gram (e.g., This Bag has Beautiful color), is fed into the model, each word of n-gram sequence is represented as a d-dimensional vector.
Recurrent neural networks (RNNs)
It is a variant of Rec NN and is used for modeling the sequential data. Sequential data is applied in a variety of applications.
RNN considers the time factor for processing the elements in a sequence.
Figure 9a shows an RNN with a loop that preserves all the information, whereas, in Fig. 9b, the unrolled version indicates that multiple copies of RNN are connected, and they communicate by passing information from one state to another

The commonly used variants of RNNs are LSTM, GRU, bi-directional RNNs, and deep RNNs.
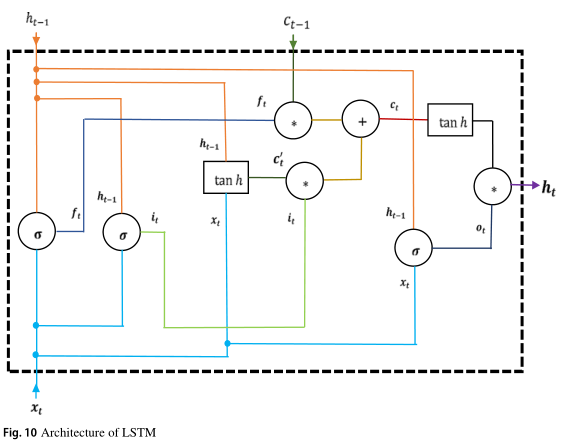
Long short-term memory(LSTM)
It is one of the most popular variants of RNN, which possesses the capability to handle the vanishing gradient problem in standard RNN and can catch long-term dependencies. This makes them more powerful and flexible. The architecture of LSTM is shown in Fig. 10.
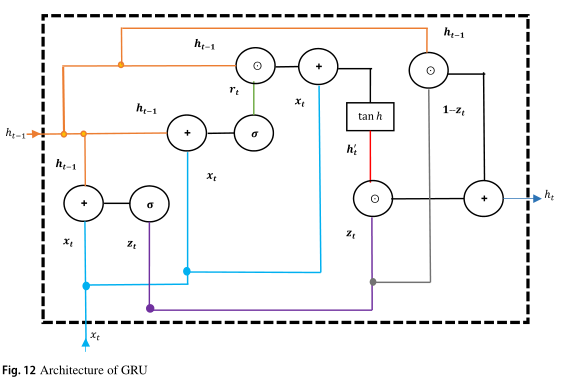
Gated Recurrent units (GRUs)
GRUs are variants of LSTM and are considered as LSTM without an output gate. The architecture of GRU is shown in Fig. 12.
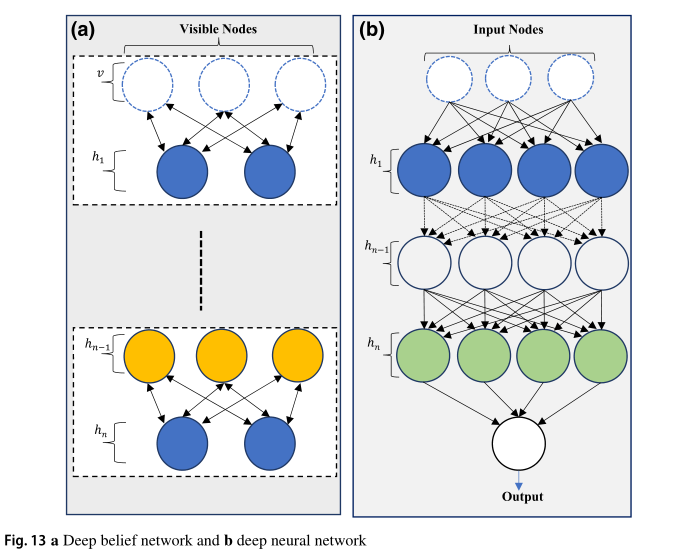
Deep belief networks (DBNs)
DBNs emanate under the type of unsupervised pre-trained networks, which also includes autoencoders and Generative Adversarial Networks. DBNs are composed of multiple layers of unsupervised networks like Restricted Boltzmann Machines (RBMs) or autoencoders as shown in Fig. 13a.
Drawbacks of deep learning approaches in sentiment analysis
Although, deep learning algorithms have shown excellent outcomes and significant evolution in sentiment analysis, yet there exist some drawbacks of applying these algorithms which are stated as follows:
-
Most deep learning techniques require a lot of labeled data for training to make sure that machine delivers the desired results. Hence, for sentiment analysis, we require a large corpus to properly train the deep learning model for correct prediction of class labels. Gathering and labeling large amounts of data can be very difficult and tedious.
-
Unlike traditional machine learning or lexical methods where we know what features are selected for predicting a particular sentiment, it is hard to figure out what is the actual reason for the neural network to predict a specific to get an intuition about the prediction process of the neural networks, and they behave like a “black box” to many researchers.
-
Deep learning techniques like CNN requires tuning of initial parameters as a starting point. This can be seen in Stojanovski et al. (2015). Thus, the performance of the network depends upon the values of the hyperparameters of the network. Hence, deciding the optimal hyperparameter values is a challenging task
-
Due to a large number of parameters present in the deep learning models, the time taken to train them is often very large (Dufourq and Bassett 2017). Moreover, they need high performing hardware like GPUs and large RAM for better efficiency.